Traditional vs Simplified Chinese Characters: Key Differences Explained
learn the difference between 繁体字 (fántǐzì) and 简体字 (jiǎntǐzì)
Choosing Between Traditional and Simplified Chinese Characters: Key Differences
Taking a Chinese course in China is a huge commitment. Here, we answer some of the common questions you might face when beginning your journey! One of the most important questions is: Which type of Chinese characters should you learn? Traditional or Simplified Chinese characters? Let’s take a look at the differences between them.
Traditional vs Simplified Chinese Characters: What’s the Difference?
First of all, Simplified Chinese characters are commonly used in Mainland China and Singapore. In contrast, Traditional Chinese characters are primarily used in Taiwan and Hong Kong. Therefore, whether you should choose to study Simplified Chinese or Traditional Chinese really depends on where you plan to stay.
When it comes to Chinese character learning, understanding these differences is crucial. It will help you decide which system to focus on when you begin your journey to learn Chinese characters effectively.
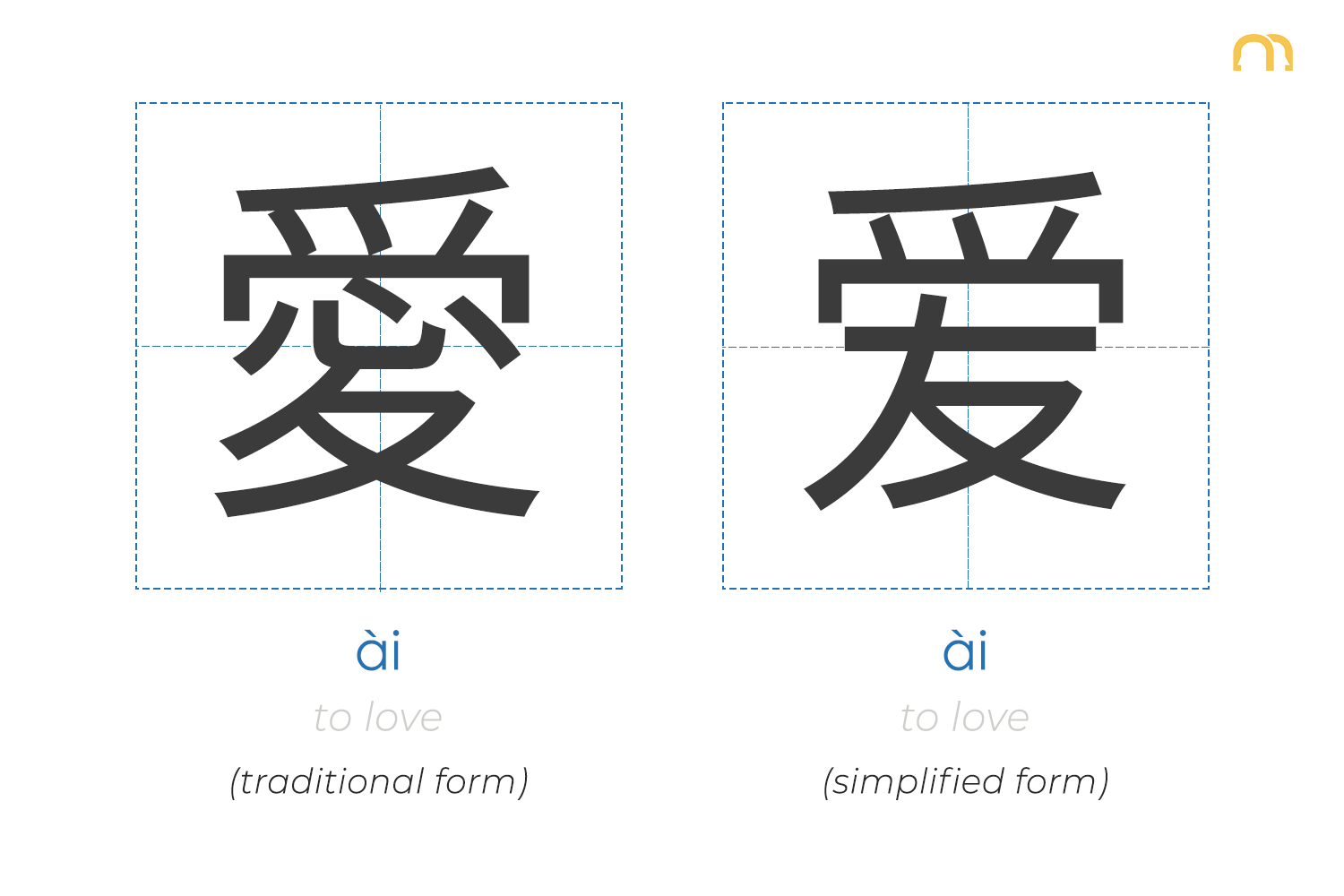
How They Look
The Chinese written language can be represented using either simplified Chinese characters or traditional Chinese characters. To learn Chinese characters, it’s important to understand the difference between traditional and simplified systems.

How They Sound
The pronunciation of both simplified and traditional characters is exactly the same if we are talking about standard Chinese (Putonghua). So, the difference lies in the writing system, which is primarily based on different geographic locations. This is important to consider when choosing characters to learn for Chinese.
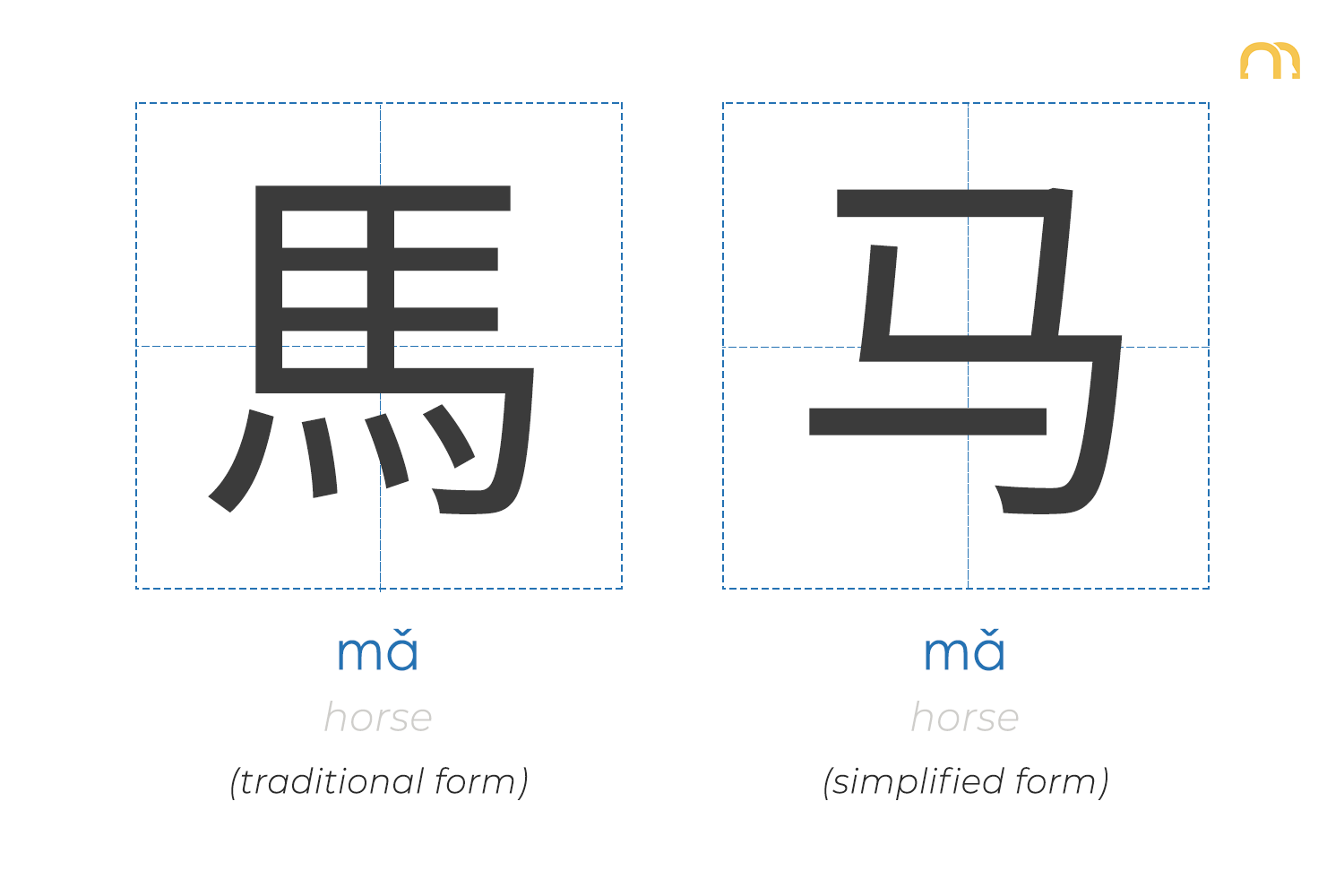
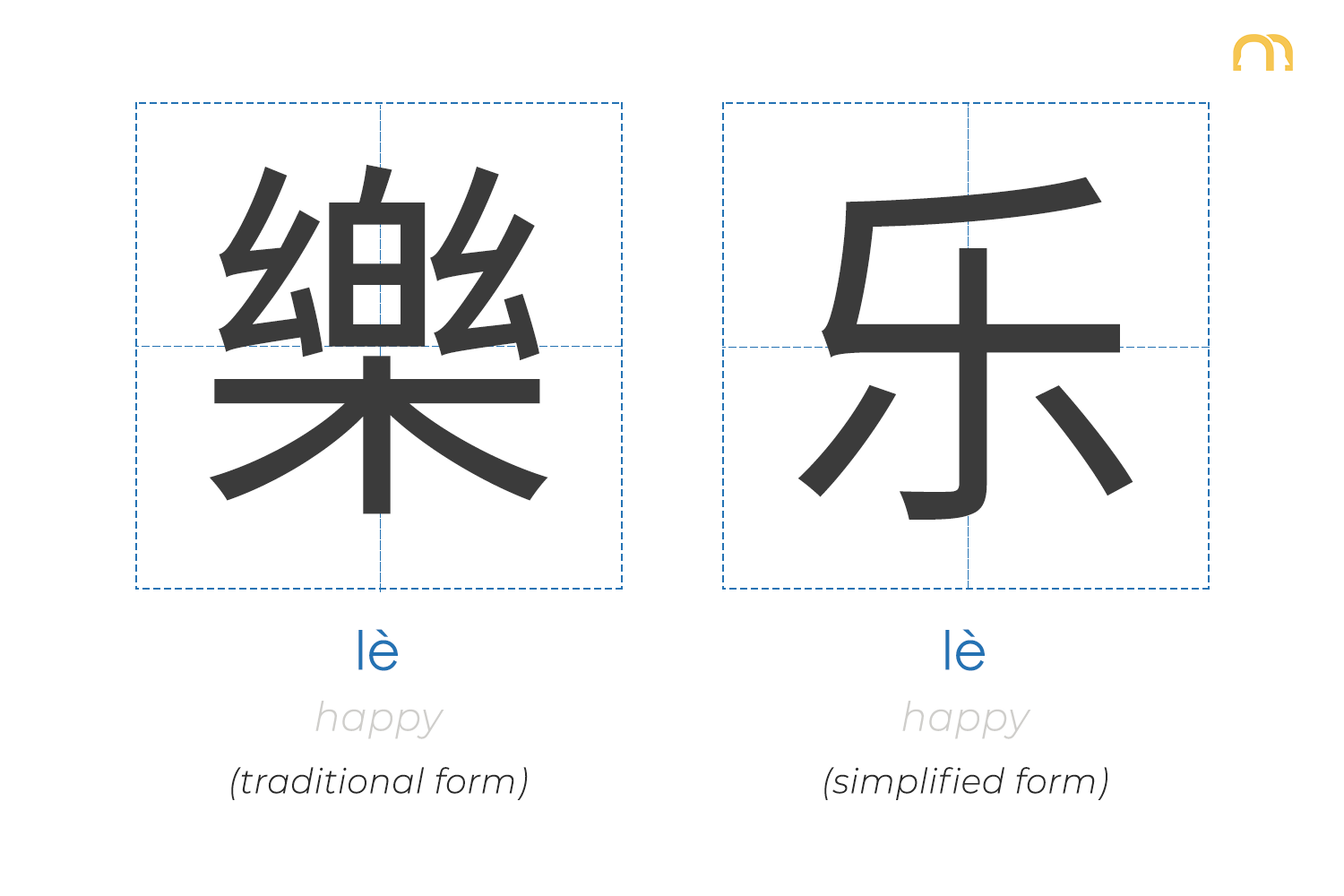
Good to Know
Traditional vs Simplified Chinese Characters
Which Type of Chinese to Learn? Mainland Mandarin vs. Taiwanese Mandarin
Some foreigners choose to study Chinese abroad in Taiwan to pursue their careers, which is also a great option. Although people in both Mainland China and Taiwan speak standard Chinese (Putonghua), there are still a couple of differences between “Mainland Chinese” and “Taiwanese Chinese.” If you’re considering Traditional vs Simplified Chinese for travel, it’s important to know which form of Chinese you’ll encounter in different regions. If you’re asking yourself, “Should I learn Traditional or Simplified Chinese?” the answer depends on your destination and purpose.

Chinese Characters
Firstly, as we’ve already mentioned, people in Mainland China use Simplified Chinese characters to represent the written language. At the same time, Traditional Chinese characters can be seen everywhere across Taiwan. Understanding these differences is essential when considering how to choose Chinese characters for learning, especially if you plan to travel or study in either region.

Accents & Intonation
Second, you may notice that people from Mainland China and people from Taiwan speak differently. It’s mainly about accents and intonation. Some people think that “Mainlanders” speak Chinese more emotionally. When it comes to Taiwan, “unaccustomed gentleness” can be perceived in their spoken Chinese. These regional differences are part of the broader Chinese writing systems explained, highlighting not just the written form but also how accents and tone shape the language.
Different Words
Third, people from Mainland China and Taiwan sometimes use different words to describe the same object. For example, the word “pineapple” in Mainland China is expressed as 菠萝 (bōluó), whereas in Taiwan it’s expressed as 凤梨 (fènglí). Another example can be “kiwi fruit”; people in Mainland China tend to call it 猕猴桃 (míhóutáo), whereas in Taiwan it’s called 奇异果 (qíyìguǒ). This is an important distinction when considering Traditional vs Simplified Chinese for communication, as vocabulary choices can affect how effectively you communicate in different regions.




